Do you know what bursitis and tendonitis are, or what differentiates them? These two conditions are fairly common and consist of the inflammation of the soft tissues around the bones and muscles. These musculoskeletal disorders mainly affect the wrists, elbows, shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles.
If you are not a healthcare professional, it might be difficult to identify which diagnosis of the bursitis or tendonitis is plaguing you. In fact, these medical conditions have so many similar and overlapping symptoms that many people use those terms interchangeably. However, there are several differences between tendonitis and bursitis and the way to treat them.
Our doctors specializing in medical imaging and musculoskeletal disorders are happy to help you learn the differences between these two conditions. Find out everything you need to know about tendonitis and bursitis.
Bursitis or Tendonitis: What Differentiates Them?
The main difference between bursitis and tendonitis is the affected tissues. While symptoms are similar, these musculoskeletal disorders do not affect the same structures.
Bursitis Definition
Bursitis is the inflammation of the fluid sack, also called bursa, that acts as a shock absorber between the bones, tendons, and muscles around a bone. The bursa’s role is thus to decrease friction and protect the structure around the bones.
Bursae are essential to help tendons slide over bones. However, not all tendons have a bursa. Bursae usually form around bony prominence, such as the level of the shoulder, the outside of the hip, or the kneecap.
Tendonitis Definition
Tendonitis is the inflammation of tendons. A tendon is a fibrous tissue that links muscles and bones. The tendon acts like a winch and allows the bone to move whenever you move or rest a muscle. The majority of cases of tendonitis are usually located at the wrist, elbow, or shoulder.
What Causes Bursitis or Tendonitis?
Tendonitis has several triggers. Repetitive movements or acute injuries are the leading causes.
Bursitis can also be caused by repetitive movements or acute injuries and by underlying conditions such as diabetes, gout, infections, or rheumatoid arthritis.
The Common Symptoms Between Tendonitis and Bursitis
These musculoskeletal disorders have several symptoms in common, such as
- Redness on the skin of the affected area
- Swelling
- Sensitivity
- Acute pain
- A feeling of warmth to the skin around bursitis or tendonitis
How to Get a Diagnostic?
Your doctor will start by asking questions about your medical history and the origin of your pain.
He will also ask you when you began to feel pain and if it is related to a specific event or if the pain increases during your activities. Your doctor will also ask if you have had surgery in the affected area.
After discussing your medical background, your doctor will proceed to a physical exam. He will look at the affected area for redness, heat, or swelling. Your doctor will also be looking for bumps under the skin, which could indicate bursitis. He will then gently move the affected limb to determine whether tendonitis limits your movements.
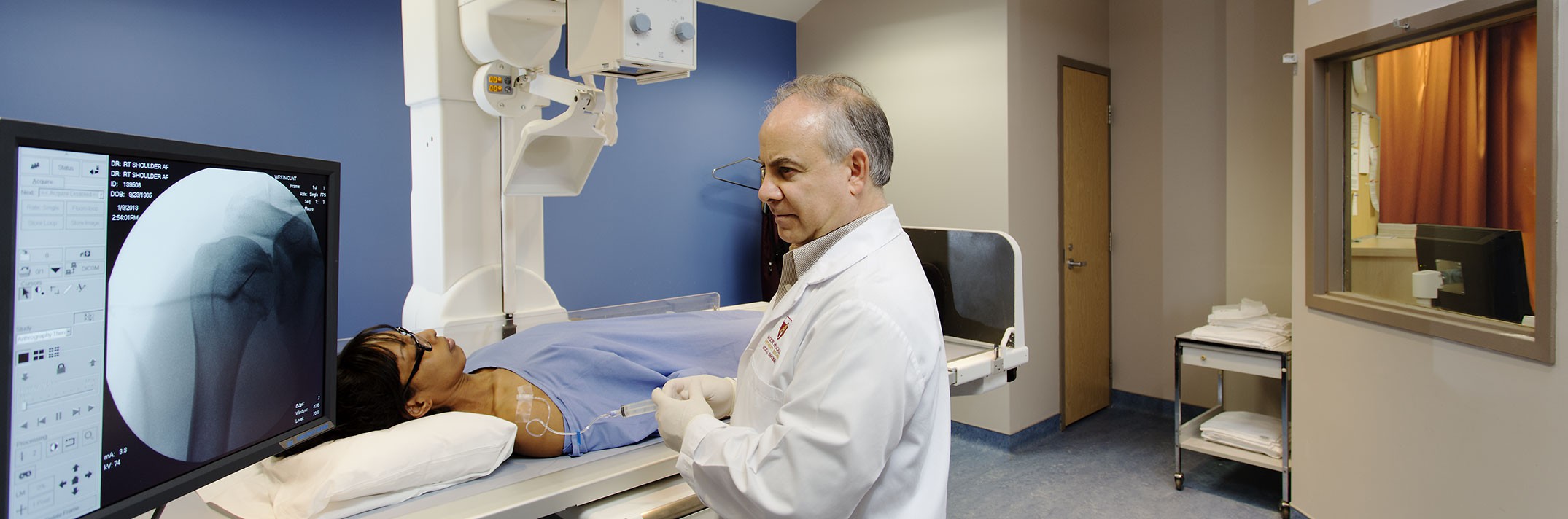
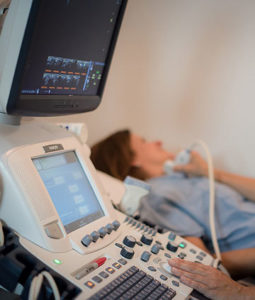
Finally, your doctor might refer you for a medical imaging examination tailored to your condition, such as an ultrasound, arthrography, MRI, or CT Scan. This examination will allow your doctor to have a clear image of your inflammation and to give you a more in-depth diagnosis.
What Are the Treatments?
There are several ways to treat bursitis and tendonitis. Treatments can be as light as resting the involved limb until resolution or surgery in the most extreme cases. So, how to heal bursitis or tendonitis?
Besides rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medication, and physiotherapy, it is possible for your doctor refer you for corticosteroid injections (infiltrations). These injections are typically performed under ultrasound or fluoroscopy.
How to Prevent Bursitis or Tendonitis?
To avoid elbow bursitis, wrist bursitis, or subacromial (shoulder) bursitis, we recommend avoiding repetitive movements and ensuring proper warm-ups prior to practicing any sports.
If you work in a field that requires repetitive motions, take breaks and let your limbs rest. Using knee protectors and wrist braces also helps prevent these musculoskeletal disorders.
You can also use these methods for shoulder tendonitis, elbow tendonitis, and wrist tendonitis. Pay attention to your body. Whenever you feel pain, it is your body telling you it is time to stop.
If you have a referral from your doctor, do not hesitate to contact us for your medical imaging exams, such as ultrasound, MRI, arthrography, and CT scans interpreted by our experienced radiologists.
Those services are available in the following clinics: Radimed West-Island, Westmount Square, Vaudreuil-Dorion, and Valleyfield. We invite you to visit our website at www.radimed.ca for more information.